What’s aluminum PCB?Structure of aluminum PCB
PCB (printed circuit board) with copper layers on one side and aluminum on the other is commonly referred to as aluminum PCB (or the most widely used PCB). The dielectric between these two layers makes it different from the traditional copper foil-based PCBs and a good heat dissipator.
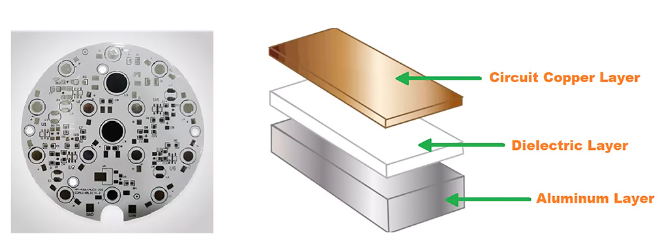
If we zoom into its structure, the aluminum PCB is just a thin metal sheet with holes punched into them. These holes are where the components go—the contacts between the circuit board and whatever device it’s connected to.
Structure of aluminum PCB
Components that make aluminum PCBs are copper, aluminum, and an insulator.
The copper is what makes up most of the board’s mass, and it conducts electricity efficiently.
The aluminum is where current flows through the board, and it helps to create a solid connection between the copper and the insulator.
Finally, the insulator prevents short circuits from forming between these pathways.
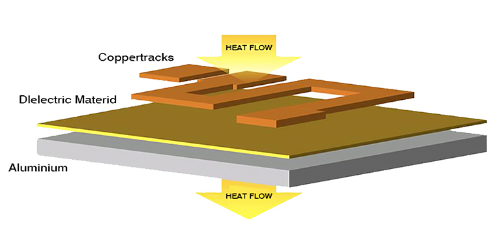
This PCB flows heat away from the system by conducting it away from the area where you want to keep it.
Here, aluminum conducts heat rapidly, so it’s great at conducting away heat. While copper conducts heat slowly but more efficiently than aluminum, so it can help transfer more heat at once. Insulation is used to prevent electrical shorts when a lot of current flows through a circuit.
What are the types of aluminum PCBs?
Through-hole aluminum PCBs
They are made of a large number of through holes drilled into the board. The holes make it easy to connect different parts of the circuit together without having to rely on soldering connections between each piece of electronic equipment that you need to connect together.
Flexible aluminum PCBs
They are known for providing excellent electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, and exceptional flexibility. They are used in applications that require flexibility, such as circuit boards that need to bend easily.
Multilayer aluminum PCBs
Multilayer aluminum PCB is made of multiple layers of materials, such as epoxy resin, which allows for greater protection against corrosion and wear from vibration than conventional lead-free solder joints could achieve on their own.
Hybrid aluminum PCBs
Hybrid Aluminum PCB is made from two different types of materials: one layer is made out of copper foil, while the other layer is made out of aluminum foil. These boards are often used for circuit boards that require both conductors and insulators.
Benefits and limitations of aluminum PCBs
Benefits of aluminum PCBs
Excellent thermal conductivity: makes it ideal for dissipating heat from high-power components, such as in LED lighting and power supplies.
Durability and reliability: make them suitable for a wide range of applications, including in harsh environments.
Cost-effective: generally less expensive to produce than traditional PCBs.
Lightweight: ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as in aerospace and automotive electronics.
Limitations of aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCBs offer few design options than traditional PCBs.
Has a higher electrical resistance which can cause issues with signal integrity and high-speed circuits.
Limited availability of design software and manufacturing capabilities.
Due to aluminum PCB heat dissipation ability, it is a useful part of different electronic applications. But the most common are:
High-power LED lighting
Automotive electronics
Power supplies
Telecommunications equipment
Industrial control systems
Medical devices
Military and aerospace applications
Electronic components are attached to aluminum PCBs in the above applications because the metal provides a stable and thermally conductive surface.
How is an aluminum PCB manufactured?
The process of manufacturing an aluminum PCB typically involves several steps.
First, a layer of thermally conductive material, such as ceramic or metal, is bonded to the aluminum base using a high-temperature adhesive.
Then, a layer of insulating material, such as epoxy or polyimide, is applied over the thermally conductive layer to provide electrical isolation.
Next, the PCB is drilled with holes to accommodate the electronic components that will be mounted on it.
Finally, the PCB is coated with a solder mask layer and printed with the desired circuit pattern using a photolithography process.
Manufacturing of this type of board is referred to as metal-core printed circuit boards (MCPCB) in which metal is used as a base of the product.
Challenges and solutions in aluminum PCB manufacturing
One of the main challenges is ensuring that the thermally conductive layer is properly bonded to the aluminum base. To address this challenge, manufacturers must carefully control the temperature and pressure of the bonding process to ensure a strong and reliable bond.
Another challenge in aluminum PCB manufacturing is drilling holes for electronic components. To overcome this challenge, manufacturers can use specialized drilling equipment and techniques, such as laser drilling or micro-drilling, to create precise and high-quality holes in the PCB.
在线留言询价
- 一周热料
- 紧缺物料秒杀
| 型号 | 品牌 | 询价 |
|---|---|---|
| MC33074DR2G | onsemi | |
| TL431ACLPR | Texas Instruments | |
| RB751G-40T2R | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BD71847AMWV-E2 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| CDZVT2R20B | ROHM Semiconductor |
| 型号 | 品牌 | 抢购 |
|---|---|---|
| TPS63050YFFR | Texas Instruments | |
| IPZ40N04S5L4R8ATMA1 | Infineon Technologies | |
| ESR03EZPJ151 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BU33JA2MNVX-CTL | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| STM32F429IGT6 | STMicroelectronics | |
| BP3621 | ROHM Semiconductor |
- 周排行榜
- 月排行榜
AMEYA360公众号二维码
识别二维码,即可关注


请输入下方图片中的验证码:


























