- Ameya360 Component Supply Platform >
- Trade news >
- Ameya360:The A-to-Z Guide on Using Stiffener for Flex and Rigid-flex PCBs
Ameya360:The A-to-Z Guide on Using Stiffener for Flex and Rigid-flex PCBs
Lighter electronics with shrinking packages are a reality today mainly due to the emergence of flexible printed circuits (FPC). They are built on materials that can bend smoothly and improve the product’s resistance to vibration and motion. FPCs reduce interconnection defects by minimizing the connection points on the PCB. Their ability to fit in unusual shapes has largely accelerated the miniaturized designs.
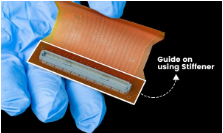
With all these advantages, the demand for flex and rigid-flex PCBs has amplified in almost all electronics business sectors. But the material agility makes the flex PCBs susceptible to quick breakdown. A supporting mechanism like a stiffener is hence recommended during the assembly of flex and rigid-flex PCBs to improve the board strength and rigidity.
What stiffeners and why they are needed in flex and figid-flex PCBs
PCB stiffeners are the mechanical parts used during the assembly process to improve the strength of Flex PCBs. They enhance the durability of the PCB by reinforcing the areas in which components will be mounted. Stiffeners add thickness to the board with an impact on cost and manufacturing time in PCB production. Even Rigid-flex PCBs are benefitted from extra strengthening by adding such stiffeners.
They are more often required when the components are in the dynamic areas of the Flex PCBs. Stiffeners are used to avoid stress on the flex boards due to heavy components. There can be pressure on the pads if the connectors require frequent plug-in/plug-out. Stiffeners can hold the PCB surface flat and strong to mount SMT parts efficiently in SMT assembly. They provide the mechanical strength to sustain vibration and shock in harsh operating environments.
Stiffeners facilitate better handling of thin and flexible boards. If there is a requirement for Zero insertion force (ZIF) connectors in the design, they can support the same. Stiffeners improve the bend radius of the PCB and also reduce the stress at flex and rigid circuit junctions. So, they are an integral part of flex and rigid-flex PCBs.
Choose the PCB stiffeners with the right material
Based on the functionality different materials are used to make stiffeners. A PCB busbar is a board stiffener that can conduct electricity. It is made using conductive metals like copper, stainless steel, or aluminum. Non-metal stiffeners are made using polyimide or FR4 material.
FR4 is the common type used for PCB stiffeners in Flex PCB applications. The main purpose of using an FR4 stiffener is to provide the required support for the PCB during the assembly processes like pick-n-place of components and in reflow ovens. They also strengthen the board in areas where connectors and other through-hole parts are mounted. The usual thickness of FR4 stiffeners varies from 0.2mm to 1.5mm. They are more affordable in price compared to other types of stiffeners.
Metal stiffeners like stainless steel or aluminum are highly recommended in applications requiring rigid-flex PCBs to operate in varied temperature ranges. They are a perfect choice in applications demanding corrosion-resistant FPCs. But they are expensive and have a longer bonding process compared to other stiffener materials. Yet, aluminum is ideal for applications involving high thermal dissipation, and stainless-steel stiffeners offer enough support within smaller spaces. While stainless steel stiffeners are available in the thickness range of 0.1mm to 1.5mm, aluminum stiffeners’ thickness can be between 0.2mm to 1.5mm.
Polyimide stiffeners are made from high-temperature polymer sheets in thicknesses ranging from 0.05mm to 0.25mm. They provide exceptional solder resistance and added bond strength. Polyimide stiffeners limit the PCB bending in specific areas while preparing the boards for final assembly. They are best suited to increase the ZIF connector thickness with additional support to contact fingers on the circuit board.
How to mount the stiffeners on flex PCBs
While assembling the stiffeners on a PCB, there are a few key factors to consider. In boards using through-hole parts, it is recommended to position the stiffener on the same side as the components to provide easy access to the solder pads on the PCB. To relieve the stress, there should be around 0.762 mm of overlap of the stiffener on the exposed coverlay of the flex PCBs. If multiple stiffeners are used, then the same stiffener thickness has to be maintained.
To ensure proper alignment, FR4 stiffener holes are enlarged by around 0.3mm as compared to flex board holes. FR4 stiffeners are mounted on the array border to ruggedize the assembly array. This can assist in the automated assembly of flex PCBs similar to rigid PCBs. Also, the need for further tooling plates can be eliminated.
Stiffeners are mounted on the flex PCBs using either pressure-sensitive adhesives or thermally bonded adhesives. Pressure-sensitive adhesives are used in IPC class 2 products while thermally bonded adhesives are preferred in application-critical IPC class 3 products. Thermal bonding adhesives provide strong bonding of stiffeners to the PCB and are expensive. They damage the board significantly if the stiffeners have to be removed. Hence, the application process is quite crucial. On the contrary, pressure-sensitive adhesives are low-cost with medium bond strength. The PCB damages can be avoided with the careful removal of bonded stiffeners while using pressure-sensitive adhesives.
Can stiffeners improve PCB performance?
Using stiffeners in Flex and Rigid-flex PCBs offers several advantages in the overall performance of the product. They provide structural support in fragile areas of flex PCBs and minimize mechanical deformities like bending and warping. Also, they avoid any possible electrical shorts in the stacked PCBs of a chassis.
In harsh environments, stiffeners protect PCBs against pressure and vibration. They can also avoid mounting screws or rivets on PCBs, reducing the cost of such additional fittings. Using busbars can improve the power distribution for the ground circuit of the PCB. They can assist in quick thermal dissipation in high-temperature applications. Thus, stiffeners are remarkable in improving the overall performance and structural integrity of the FPCs.
Conclusion
To control the cost and quality of flexible printed circuits, it is important to work with an experienced contract manufacturer (CM). Building stiffener PCBs with optimized quality and reduced cost is possible if your CM has adopted quality management guidelines and is equipped with the latest technologies in the production line. Further, this comprehensive guide on stiffeners will enable you in understanding the right choice of material, adhesive types, key mounting considerations, and their usage in Flex and Rigid-flex PCBs.
Online messageinquiry
What is “component placement” in PCB?

15 Common PCB Circuit Effects
- Week of hot material
- Material in short supply seckilling
| model | brand | Quote |
|---|---|---|
| RB751G-40T2R | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BD71847AMWV-E2 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| MC33074DR2G | onsemi | |
| TL431ACLPR | Texas Instruments | |
| CDZVT2R20B | ROHM Semiconductor |
| model | brand | To snap up |
|---|---|---|
| IPZ40N04S5L4R8ATMA1 | Infineon Technologies | |
| BU33JA2MNVX-CTL | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| STM32F429IGT6 | STMicroelectronics | |
| TPS63050YFFR | Texas Instruments | |
| ESR03EZPJ151 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BP3621 | ROHM Semiconductor |
- Week of ranking
- Month ranking
Qr code of ameya360 official account
Identify TWO-DIMENSIONAL code, you can pay attention to


Please enter the verification code in the image below:
























