- Ameya360 Component Supply Platform >
- Trade news >
- Aluminum-based PCB vs Ceramic-based PCB – A Comprehensive Comparison for Your Electronics
Aluminum-based PCB vs Ceramic-based PCB – A Comprehensive Comparison for Your Electronics
In the realm of electronics, the choice of printed circuit board (PCB) material plays a pivotal role in determining the functionality, performance, and longevity of electronic devices. Two prominent contenders in this domain are aluminum-based PCBs and ceramic-based PCBs, each with its distinct advantages and specialized applications. Let’s delve deeper into the characteristics, pros, and cons of aluminum-based PCB vs ceramic-based PCB to aid in your decision-making process.
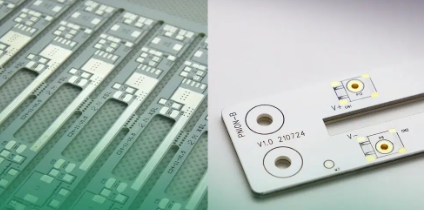
Aluminum-based PCBsAluminum-based PCBs, also recognized as metal core PCBs (MCPCBs), boast a core constructed from an aluminum alloy. These boards have garnered attention for their exceptional thermal conductivity and find extensive usage in applications that demand efficient heat dissipation.
Aluminum-based PCBs
Advantages of Aluminum-based PCBs
Thermal Conductivity: The standout feature of Aluminum-based PCBs is their remarkable thermal conductivity. This property makes them a preferred choice in applications where heat dissipation is critical, such as LED lighting systems, power converters, and automotive electronics. The ability to efficiently transfer heat away from sensitive components ensures enhanced reliability and longevity of the devices.
Cost-Efficiency: Aluminum-based PCBs often present a more budget-friendly option compared to certain high-performance materials. This cost-effectiveness makes them attractive for projects where optimizing expenses without compromising quality is a priority.
Lightweight Nature: Despite their robust construction, Aluminum-based PCBs maintain a relatively lightweight profile. This attribute proves advantageous in applications where weight considerations are pivotal, such as portable electronic devices or aerospace applications.
Manufacturing Simplicity: The manufacturing process for Aluminum-based PCBs is often simpler and more straightforward compared to some other materials, leading to reduced production time and costs.
However, these PCBs do come with their set of limitations, which might impact their suitability for specific applications.
Limitations of Aluminum-based PCBs
Electrical Insulation Requirements: Aluminum-based PCBs necessitate an insulating layer between the circuit and the metal base to prevent short circuits. This requirement adds complexity to the manufacturing process and design considerations, potentially increasing production costs.
Mechanical Strength: While durable, Aluminum-based PCBs might not offer the same level of mechanical strength as Ceramic-based PCBs. This factor could limit their use in applications exposed to harsh physical environments or substantial mechanical stress.
Ceramic-based PCBsCeramic-based PCBs, typically crafted from materials like aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride, have gained prominence owing to their outstanding electrical insulation properties and reliability in diverse applications.
Ceramic-based PCBs
Advantages of Ceramic-based PCBs
Superior Electrical Insulation: The hallmark of Ceramic-based PCBs lies in their superior electrical insulation capabilities. These boards excel in preventing signal interference and short circuits, making them ideal for high-voltage applications where maintaining signal integrity is crucial.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength: Ceramic-based PCBs exhibit greater mechanical strength compared to their Aluminum-based counterparts. This characteristic makes them well-suited for deployment in rugged environments or applications where resistance to mechanical stress is imperative.
High-Frequency Applications: With low dielectric loss and excellent signal integrity properties, Ceramic-based PCBs are highly sought after for high-frequency circuits and radio frequency (RF) applications.
Chemical Resistance: Ceramics demonstrate remarkable resistance to chemicals and corrosion, making Ceramic-based PCBs suitable for applications exposed to harsh and corrosive environments, such as in aerospace or industrial settings.
However, these boards also come with certain limitations that might influence their suitability for specific projects.
Limitations of Ceramic-based PCBs
Cost Considerations: Ceramic-based PCBs typically entail higher manufacturing costs due to the expense of materials and the complexity involved in their production. This factor might limit their feasibility for projects with stringent budget constraints.
Brittleness: Despite their mechanical strength, ceramics can be inherently brittle. Careful handling is required during production, assembly, and installation to prevent breakage, which can add to the overall project timeline and costs.
ConclusionThe choice between Aluminum-based and Ceramic-based PCBs hinges on a comprehensive evaluation of your project’s requirements, budget considerations, and the specific environmental conditions the electronic device will encounter.
For applications where thermal management and cost-effectiveness are paramount, Aluminum-based PCBs might prove more suitable. Conversely, if superior electrical insulation, mechanical robustness, and reliability in harsh conditions are essential, Ceramic-based PCBs could be the preferred option.
Ultimately, consulting with experienced PCB manufacturers or engineers remains pivotal in making an informed decision aligned with the unique demands of your electronic project.
Online messageinquiry
What is “component placement” in PCB?

15 Common PCB Circuit Effects
- Week of hot material
- Material in short supply seckilling
| model | brand | Quote |
|---|---|---|
| BD71847AMWV-E2 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| MC33074DR2G | onsemi | |
| TL431ACLPR | Texas Instruments | |
| RB751G-40T2R | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| CDZVT2R20B | ROHM Semiconductor |
| model | brand | To snap up |
|---|---|---|
| IPZ40N04S5L4R8ATMA1 | Infineon Technologies | |
| BU33JA2MNVX-CTL | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| STM32F429IGT6 | STMicroelectronics | |
| BP3621 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| TPS63050YFFR | Texas Instruments | |
| ESR03EZPJ151 | ROHM Semiconductor |
- Week of ranking
- Month ranking
Qr code of ameya360 official account
Identify TWO-DIMENSIONAL code, you can pay attention to


Please enter the verification code in the image below:
























