- Ameya360 Component Supply Platform >
- Trade news >
- Understanding Force Sensing Resistor (FSR) Technology
Understanding Force Sensing Resistor (FSR) Technology
Force Sensing Resistors (FSRs) represent a critical advancement in sensor technology, offering a versatile and efficient means of measuring force or pressure across a wide range of applications. From consumer electronics to medical devices, automotive systems to robotics, FSRs play a pivotal role in enhancing functionality, safety, and user experience. This article delves into the workings of FSRs, their applications, and the advantages they offer.
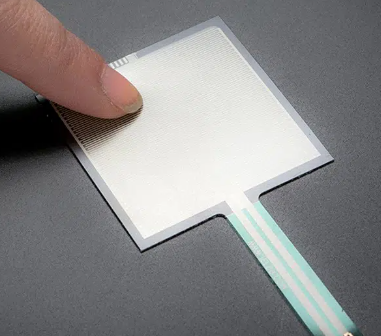
What is a Force Sensing Resistor?
A Force Sensing Resistor, also known as a pressure sensor or force-sensitive resistor, is an electronic component whose electrical resistance changes in response to applied force or pressure. Essentially, it’s a thin, flexible, polymer-based material that exhibits a decrease in resistance when pressure is applied to its surface. This change in resistance can be measured and calibrated to determine the magnitude of the applied force.
How do Force Sensing Resistors Work?The fundamental principle behind FSR operation is the conductive polymer material used in its construction. Typically, this material is embedded with conductive particles, and when pressure is applied, the distance between these particles decreases, allowing more current to flow through the sensor. This change in current flow corresponds to a change in resistance, which can be precisely measured.
What’s the applications of Force Sensing Resistors?Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): FSRs are extensively used in touch-sensitive interfaces for consumer electronics like smartphones, tablets, and touch-sensitive buttons in appliances. They enable intuitive interaction by detecting the pressure exerted by a user’s touch.
Medical Devices: In medical applications, FSRs are employed in devices such as electronic skin, prosthetics, and pressure-sensitive mats for patient monitoring. They help in measuring pressure distribution for applications like orthopedic rehabilitation or monitoring bedridden patients.
Automotive Systems: FSRs find applications in automotive technologies such as seat occupancy sensors, airbag deployment systems, and touch-sensitive controls in vehicles. They enhance safety by accurately detecting the presence and position of occupants and providing feedback for touch-sensitive controls.
Robotics: FSRs are used in robotics for force feedback systems, grip force sensing in robotic hands, and collision detection. This allows robots to interact safely and accurately with their environment, objects, and humans.
Sports Equipment: FSRs are integrated into sports equipment such as smart insoles, golf club grips, and bicycle handlebars to measure pressure distribution, grip force, and impact forces. This data can be used for performance analysis, injury prevention, and technique improvement.
What’s the advantages of Force Sensing Resistors?Flexibility: FSRs are thin and flexible, making them suitable for applications where space and form factor are constraints.
Low Power Consumption: They typically require low power to operate, making them suitable for battery-powered devices.
High Sensitivity: FSRs exhibit high sensitivity to force or pressure changes, enabling precise measurement across a wide range of forces.
Cost-Effective: Compared to other force sensing technologies like load cells or piezoelectric sensors, FSRs are often more cost-effective, making them a preferred choice for many applications.
Easy Integration: FSRs can be easily integrated into existing electronic systems due to their simple design and compatibility with standard electronic interfaces.
What are the components of Force Sensing Resistors FSR?Force Sensing Resistors (FSRs) typically consist of several components that work together to detect and measure force or pressure. These components include:
Substrate Material: FSRs are usually constructed using a flexible substrate material, often made of polymers like polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This substrate provides the foundation for the sensor and allows it to conform to curved or irregular surfaces.
Conductive Polymer: The key component of an FSR is the conductive polymer layer. This layer is typically applied to the substrate and contains conductive particles dispersed throughout a polymer matrix. When pressure is applied to the sensor, the distance between these particles decreases, leading to a reduction in electrical resistance.
Conductive Traces: FSRs often incorporate conductive traces or electrodes on the substrate, which are used to connect the sensor to external circuitry. These traces provide electrical connections for measuring the resistance of the sensor and transmitting data to a microcontroller or other electronic devices.
Protective Layer: Many FSRs feature a protective layer on top of the conductive polymer to shield it from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and mechanical damage. This protective layer may be made of materials like silicone rubber or polyimide film.
Connector: In some cases, FSRs may include a connector or terminal for easy integration into electronic systems. This connector allows for quick and secure electrical connections without the need for soldering.
Online messageinquiry
What is thin-film resistor Difference between thin-film resistors and thick-film resistors
- Week of hot material
- Material in short supply seckilling
| model | brand | Quote |
|---|---|---|
| CDZVT2R20B | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| MC33074DR2G | onsemi | |
| TL431ACLPR | Texas Instruments | |
| BD71847AMWV-E2 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| RB751G-40T2R | ROHM Semiconductor |
| model | brand | To snap up |
|---|---|---|
| ESR03EZPJ151 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BU33JA2MNVX-CTL | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BP3621 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| IPZ40N04S5L4R8ATMA1 | Infineon Technologies | |
| TPS63050YFFR | Texas Instruments | |
| STM32F429IGT6 | STMicroelectronics |
- Week of ranking
- Month ranking
Qr code of ameya360 official account
Identify TWO-DIMENSIONAL code, you can pay attention to


Please enter the verification code in the image below:























