- Ameya360 Component Supply Platform >
- Trade news >
- TE Connectivity Blind Mating Mobile Charging Connectors
TE Connectivity Blind Mating Mobile Charging Connectors
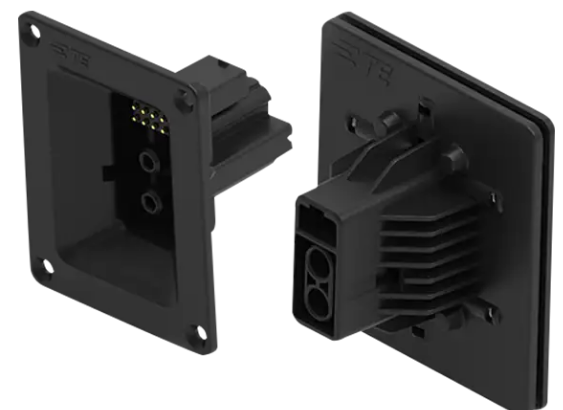
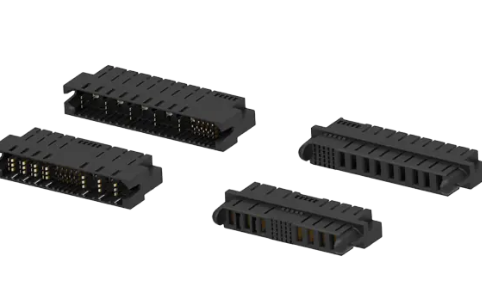
TE Connectivity's (TE) Blind Mating Mobile Charging Connectors are intended for smaller mobile robots and autonomous vehicles typically used in warehouse environments. Autonomous mobile robots (AMR) are used mostly for material handling (picking, movement, storage, and sorting) in the warehouse automation space.
TE's Blind Mating Mobile Charging Connectors are available in 2- and 3-power contact options with up to eight signal contacts to ease installation and rework cycle times. The series offers a high mating cycle life and serves as a modular solution that will support different configurations, data, and sensing.
FEATURES
Robust design for high-cycle life
Designed for a minimum of 12,000 mating cycles
Low insertion force power contacts
Spring probe signal contacts
Connection flexibility
2 and 3 power contact options
Up to 50A and up to 125V
Up to 40A per line at up to 100V
Terminates to 10AWG or 8AWG stranded copper wire
First make, last break contact for use in grounding, system enabling, or applications that require charging two battery strings independently
Touch safe contacts for extra safety if rework is needed
Blind mate capability
Allows for the misalignment of at least ±15mm for x and ±10 for the y direction
± Approx. 5° for z direction (mating)
Up to 8x signal contacts
Up to 0.5A per line
Terminates to 30AWG to 22AWG stranded wire
Rear pluggable interface to ease installation and rework cycle times
Spring probe contacts for high cycle life
Utilizes Mini Universal MATE-N-LOKII Connector interface for signal contact mating
APPLICATIONS
Charging for autonomous mobile robots/automated guided vehicles (AMR/AGV)
Blind mate battery charging
Industrial
Hospitality
Retail
Medical
Online messageinquiry
- Week of hot material
- Material in short supply seckilling
| model | brand | Quote |
|---|---|---|
| CDZVT2R20B | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BD71847AMWV-E2 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| RB751G-40T2R | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| MC33074DR2G | onsemi | |
| TL431ACLPR | Texas Instruments |
| model | brand | To snap up |
|---|---|---|
| ESR03EZPJ151 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| STM32F429IGT6 | STMicroelectronics | |
| IPZ40N04S5L4R8ATMA1 | Infineon Technologies | |
| BP3621 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| TPS63050YFFR | Texas Instruments | |
| BU33JA2MNVX-CTL | ROHM Semiconductor |
- Week of ranking
- Month ranking
Qr code of ameya360 official account
Identify TWO-DIMENSIONAL code, you can pay attention to


Please enter the verification code in the image below: