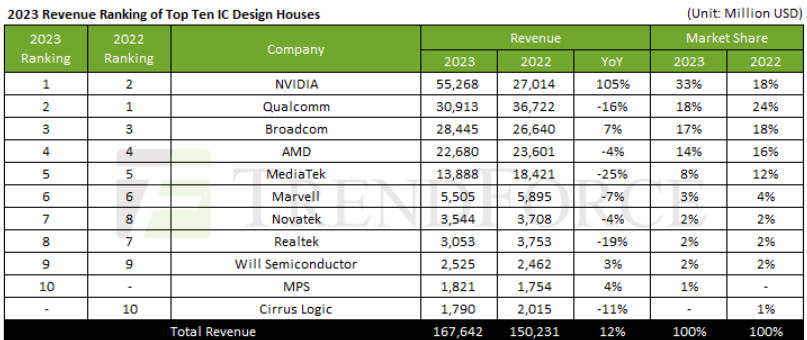
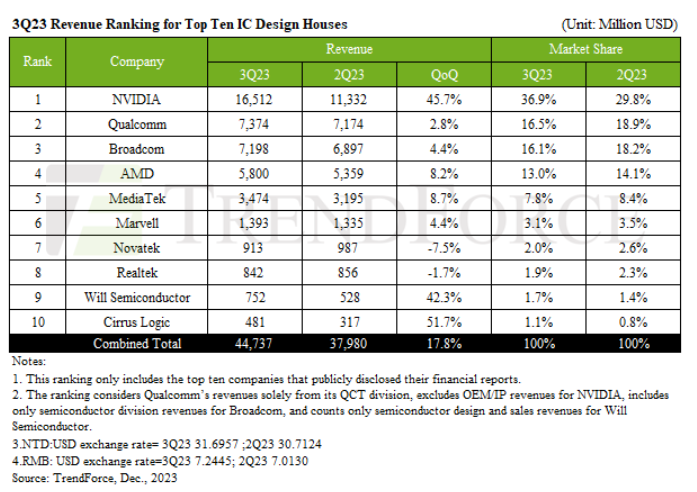
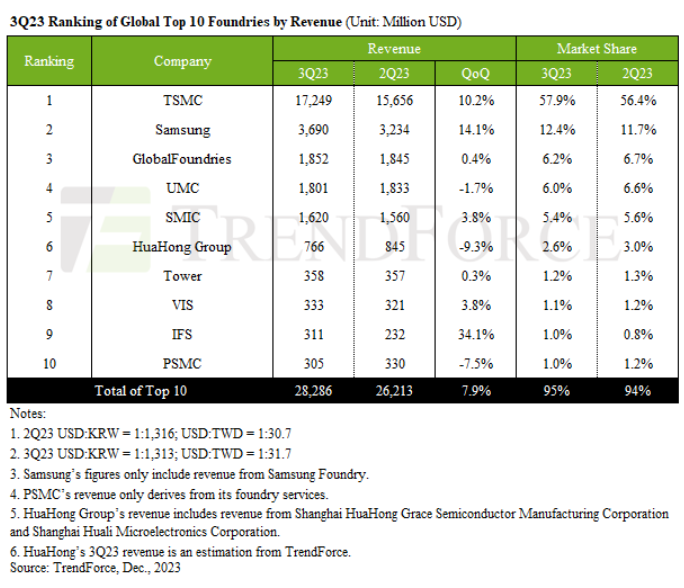
Choke Inductors What They Are and What They Do
Have you ever wondered how your phone stays charged or how your car radio delivers crystal-clear sound even on a bumpy road? The answer might lie in a tiny, unassuming component called a choke inductor. While they may not be the flashiest parts in your electronics, choke inductors are critical in ensuring smooth operation and clean power delivery across many devices. In this blog, we will look into the world of choke inductors and explain their function, work, and applications in everyday electronics.
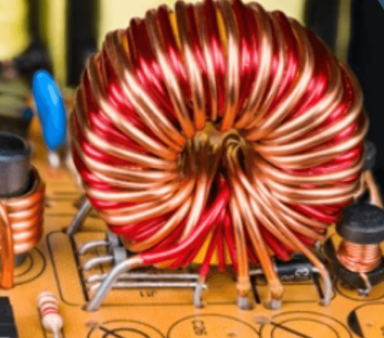
What is a Choke Inductor?
A choke inductor, also commonly referred to as a choke coil inductor or simply a choke, is a passive electronic component that acts like a gatekeeper for electrical current. Unlike its cousin, the resistor, which dissipates energy as heat, a choke inductor manipulates the current flow based on its frequency. Here's the key difference:
Choke inductors: Block high-frequency alternating current (AC) while allowing direct current (DC) and lower-frequency AC to pass through.
Resistors: Resist all current frequencies, reducing the overall current flow and dissipating energy as heat.
This selective filtering property makes choke inductors essential components in various electronic circuits, ensuring clean power delivery and mitigating unwanted electrical noise.
How Does a Choke Inductor Work?
The magic behind choke inductors lies in their ability to generate a magnetic field when current flows through their coil. This magnetic field, in turn, opposes any changes in current. Here's a breakdown:
Current Flow: When current passes through the coil's wire, a magnetic field is generated around it.
Magnetic Field Opposition: According to Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction, this magnetic field tries to resist changes in the current that created it.
Frequency Dependence: High-frequency AC signals involve rapid changes in the current direction. The opposing magnetic field substantially affects these rapid changes, making it more difficult for the high-frequency AC to pass through the choke.
DC and Low-Frequency AC: The changes in current are slower for direct current (DC) and lower-frequency AC. The opposing magnetic field has less impact, allowing these currents to pass through the choke with minimal hindrance.
Purpose of a Choke Inductor
Choke inductors offer a variety of functionalities in electronic circuits. Here are some of their essentialkey purposes:
Filtering: As mentioned, choke inductors filter out unwanted high-frequency noise from AC signals. This is crucial for ensuring clean power delivery and preventing interference with other components in the circuit.
Energy Storage: Choke inductors can store energy in their magnetic field when current flows through them. This stored energy can then be released back into the circuit when needed. This property is beneficial in circuits requiring power regulation or transient voltage suppression.
Voltage Regulation: Choke inductors can regulate circuit voltage levels with capacitors. By controlling the flow of current and the energy stored within the magnetic field, choke inductors help maintain a stable voltage output.
Types of Choke Inductors
While the basic operating principle remains the same, choke inductors come in various types based on their core material:
Air-Core Chokes: These chokes have an air core that offers low inductance (the ability to store energy magnetically) but works well at high frequencies. They are typically used in RF (radio frequency) circuits.
Iron-Core Chokes: Iron-core chokes provide higher inductance than air-core chokes, making them suitable for applications requiring more energy storage or filtering lower-frequency AC noise. However, they can suffer from core losses at higher frequencies.
Ferrite-Core Chokes: Ferrite is a ceramic material commonly used in choke inductors. It offers a good balance between inductance and core losses, making it a versatile choice for many applications, especially beneficial for high-frequency filtering applications.
Real-World Applications
Choke inductors are ubiquitous in various electronic devices:
Automotive Electronics: They play a vital role in power supplies for car audio systems, engine control units (ECUs), and other electronic components, filtering out noise and ensuring smooth operation.
Power Electronics: Choke inductors are essential in switch-mode power supplies, filtering out switching noise and regulating voltage for various electronic devices.
Radio Frequency (RF) Circuits: In RF circuits, choke inductors prevent unwanted signals from leaking out and interfering with other circuits. This ensures efficient signal transmission and reception.
Final Thoughts
Choke inductors are workhorses in electronics, silently ensuring clean power delivery, signal integrity, and protection from unwanted interference. By understanding their operating principles and various types, you gain valuable insight into the intricate workings of electronic circuits. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or an electronics enthusiast, appreciating the role of choke inductors empowers you to design and troubleshoot circuits more effectively.
在线留言询价

Unveiling the Intricacies of IC Design
- 一周热料
- 紧缺物料秒杀
| 型号 | 品牌 | 询价 |
|---|---|---|
| MC33074DR2G | onsemi | |
| CDZVT2R20B | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| BD71847AMWV-E2 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| TL431ACLPR | Texas Instruments | |
| RB751G-40T2R | ROHM Semiconductor |
| 型号 | 品牌 | 抢购 |
|---|---|---|
| TPS63050YFFR | Texas Instruments | |
| BP3621 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| ESR03EZPJ151 | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| STM32F429IGT6 | STMicroelectronics | |
| BU33JA2MNVX-CTL | ROHM Semiconductor | |
| IPZ40N04S5L4R8ATMA1 | Infineon Technologies |
- 周排行榜
- 月排行榜
AMEYA360公众号二维码
识别二维码,即可关注


请输入下方图片中的验证码: